Introduction
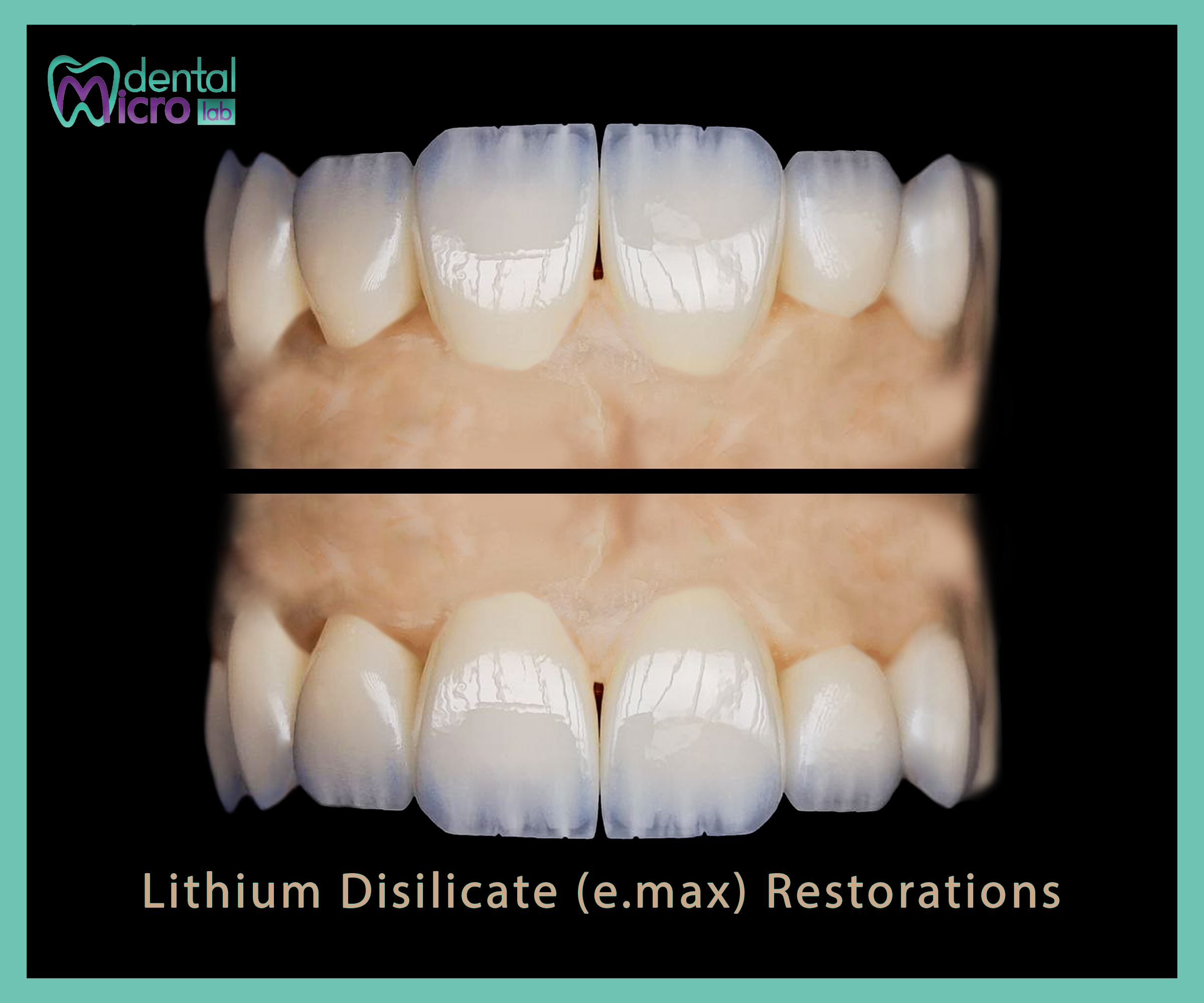
Lithium disilicate glass-ceramics (e.max) remain a top choice for anterior crowns, veneers, and conservative onlays due to excellent esthetics and predictable bonding. Long-term clinical studies demonstrate impressive survival rates, especially when restoration design and bonding protocols are optimized. For example, multi-year follow-ups report low annual failure rates and strong performance for both anterior and posterior applications.
Clinical performance & expected longevity
Large cohort studies and long-term follow-ups show lithium disilicate restorations can achieve high survival over 10+ years when properly bonded and maintained. Pressed and CAD/CAM lithium disilicate both show excellent outcomes in single crowns and partial-coverage restorations, with slightly higher failure risk for certain posterior onlays under heavy occlusal loads.
Indications & design considerations
Anterior crowns & veneers: ideal for maximum esthetics (translucency, color matching).
Posterior onlays/inlays: conservative option but ensure adequate thickness and occlusal design to withstand functional loads.
Preparation: follow conservative minimal-prep principles when possible; provide adequate bonding surface (enamel when feasible).
Bonding protocol (essentials)
Etch the internal surface: Hydrofluoric acid (per manufacturer instructions) to create microretentive surface.
Silane coupling: Apply silane agent to convert silica-rich surface for chemical bond with resin cement.
Adhesive dentistry on tooth: Standard adhesive protocol to enamel/dentin (etch-and-rinse or reliable self-etch).
Resin cementation: Use resin cements compatible with pre-treated lithium disilicate.
This adhesive approach is a major reason for excellent long-term results in the literature.
Practical tips for longevity
Control occlusion carefully; consider night guards for bruxers.
Use digital shade-matching and try-in procedures to avoid remakes.
Schedule regular maintenance and hygiene recalls.
References
Long-term clinical study on pressed e.max survival.